|
The Great
Lakes 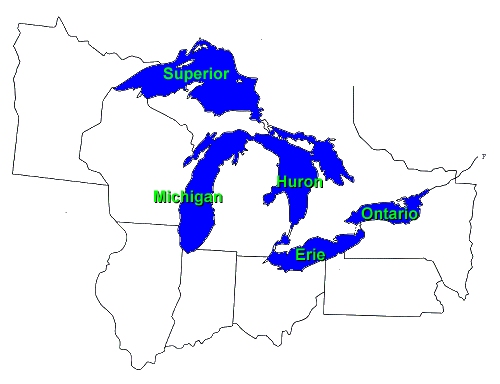
The Laurentian Great Lakes were formed nearly 20,000 years ago when the
earth's climate warmed and the last glacial continental ice sheet
retreated. The glacier, up to 2 miles thick, was so heavy and powerful it
gouged out the earth's surface to create the lake basins. Meltwater from
the retreating glacier filled the newly created basins. Approximately
3,500-4,000 years ago, the Great Lakes attained their modern levels and
area.
Water Volume:
5,500 cubic miles (22,809 cubic km), 90% of U.S. supply, 18% of world
supply
Water Surface Area:
95,000 square miles (245,759 square km). Largest surface area of
freshwater in the world.
Shoreline Length:
10,210 miles (17,017 km).
Shoreline Use:
- Residential - U.S.
26.5%, Canada 18.6%;
- Commercial /
Industrial - U.S. 6.7%, Canada 2.6%;
- Agricultural - U.S.
1.5%, Canada 8.2%;
- Other - U.S. 65.3%,
Canada 70.6% (Canada includes transportation/communications,
recreation, extraction, water, wetlands, forestry, grassland, barren;
U.S. includes public, beaches, forests, barren lands)
Population:
35 million.
Outlets:
St. Lawrence River and Chicago Sanitary & Ship Canal
Retention Times
(amount of time it takes for lakes to get rid of pollutants):
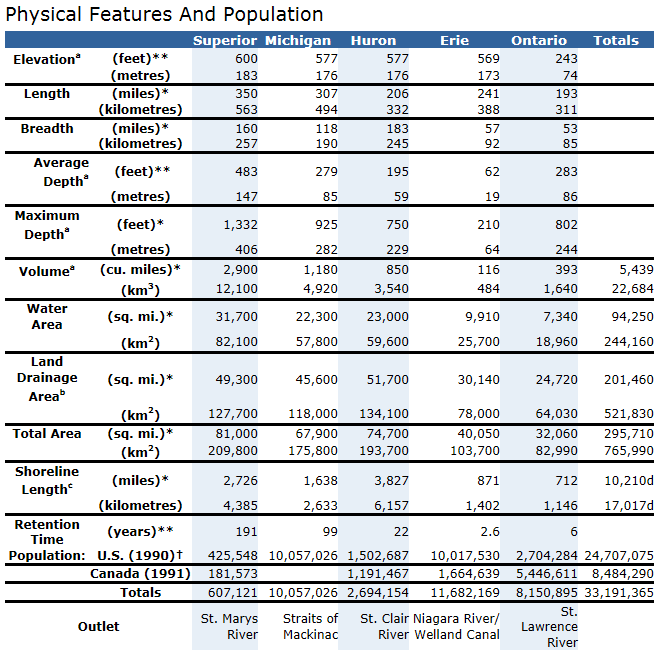
- Lake Superior: 191
years
- Lake Michigan: 99
years
- Lake Huron: 22 years
- Lake Ontario: 6 years
- Lake Erie: 2.6 years
$4 billion sports fishery
industry.
250 species of fish.
Provides drinking water for
40 million people. Provides 56 billion gallons of water per day for
municipal, agricultural, and industrial use.
Commercial shipping of 200
million tons over 1,270 mile route.
Provides power generation
and cooling water.
Produces 90% of iron ore.
The Great
Lakes - Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie and Ontario - are a dominant part
of the physical and cultural heritage of North America. Shared with Canada
and spanning more than 750 miles (1,200 kilometers) from west to east,
these vast inland freshwater seas have provided water for consumption,
transportation, power, recreation and a host of other uses.
The Great
Lakes are the largest surface freshwater system on the Earth. They contain
about 84 percent of North America's surface fresh water and about 21
percent of the world's supply. Only the polar ice caps contain more fresh
water.
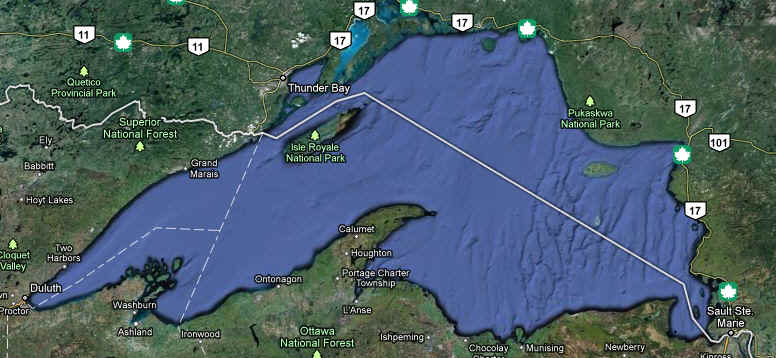
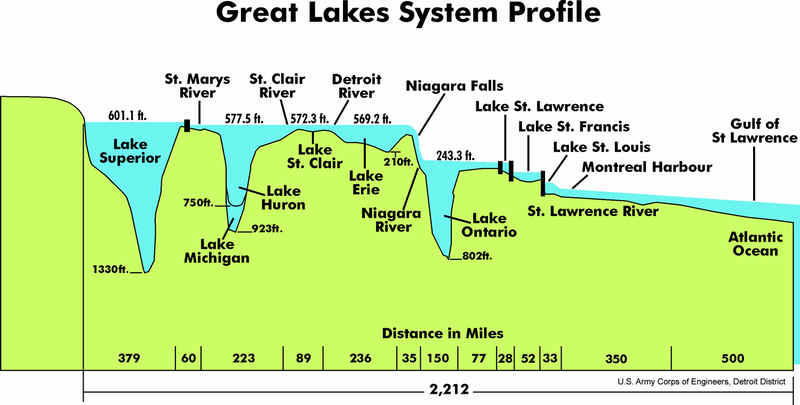
- Lake Superior is 1,335
feet deep and 350 miles long. It is the largest of the Great Lakes in
both surface area and volume. Lake Superior is the largest in terms of
volume. It is also the deepest and coldest of the five. Because of its
size, Superior has a retention time of 191 years. Retention time is a
measure based on the volume of water in the lake and the mean rate of
outflow. Most of the Superior basin is forested, with little agriculture
because of a cool climate and poor soils. The forests and sparse
population result in relatively few pollutants entering Lake Superior,
except through airborne transport.
Lake
Superior Basin Statistics
| Length |
350 mi / 563 km
|
| Breadth |
160 mi / 257 km |
| Depth |
489 ft / 149 m
average
1,333 ft / 406 m maximum
|
| Shoreline Length |
2,730 miles / 4393
km (including islands) |
| Volume |
2,935 cubic mi /
12,232 cubic km |
| Water Surface Area |
31,700 square
miles /
82,097 square km |
|
Retention/Replacement Time |
191 years |
| Outlet |
St. Marys River
to Lake Huron
Levels regulated
by international agreements
|
| Surface Area in
U.S. |
20,598 square
miles / 53,350 square km |
| Population |
444,000 U.S. /
229,000 Canada |
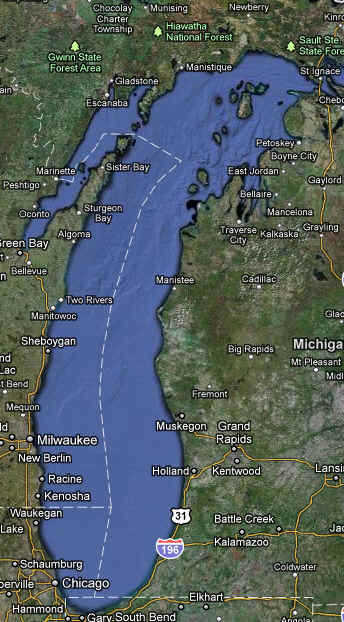
- Lake Michigan is 925
feet deep and 307 miles long. It is the third largest Great Lake and the
sixth largest freshwater lake in the world. Lake Michigan, the second
largest, is the only Great Lake entirely within the United States. The
northern part is in the colder, less developed upper Great Lakes region.
It is sparsely populated, except for the Fox River Valley, which drains
into Green Bay. This bay has one of the most productive Great Lakes
fisheries but receives the wastes from the world's largest concentration
of pulp and paper mills. The more temperate southern basin of Lake
Michigan is among the most urbanized areas in the Great Lakes system. It
contains the Milwaukee and Chicago metropolitan areas. This region is
home to about 8 million people or about one-fifth of the total
population of the Great Lakes basin
Lake
Michigan Basin Statistics
|
Length
|
307 mi / 494 km
|
|
Breadth
|
118 mi /190 km
|
|
Depth
|
279 ft / 85 m average
923 ft / 281 m maximum
|
|
Volume
|
1,180 cubic mi /
4,918 cubic km
|
|
Shoreline Length
|
1,640 mi
/ 2,639 km (including islands)
|
|
Water Surface Area
|
22,300 square mi /
57,753 square km
|
|
Surface Area in U.S.
|
22,300 square mi /
57,753 square km
|
|
Retention/Replacement Time
|
99
years
|
|
Outlet
|
Straits of Mackinac to Lake Huron
|
|
Population
|
12,052,743 U.S.
|
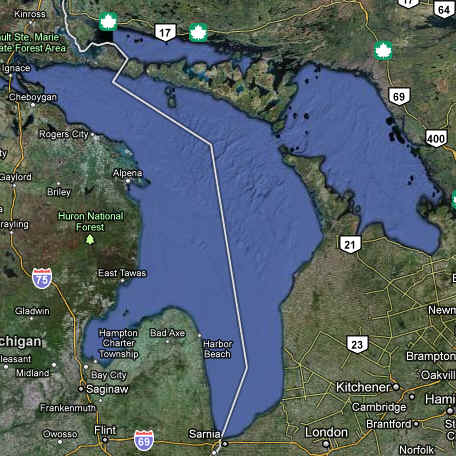
- Lake Huron is 748 feet
deep and 206 miles long. It is the second largest Great Lake and the
fifth largest freshwater lake in the world. It has the longest shoreline
of the Great Lakes if you count the shorelines of its 30,000 islands.
Lake Huron, which includes Georgian Bay, is the third largest of the
lakes by volume. Many Canadians and Americans own cottages on the
shallow, sandy beaches of Huron and along the rocky shores of Georgian
Bay. The Saginaw River basin is intensively farmed and contains the
Flint and Saginaw-Bay City metropolitan areas. Saginaw Bay, like Green
Bay, contains a very productive fishery
Lake
Huron Basin Statistics
| Length |
206 mi / 332 km |
| Breadth |
183 mi / 295 km |
| Depth |
195 ft / 59 m
average
750 ft / 229 m maximum
|
| Volume |
849 cubic mi /
3,538 cubic km |
| Shoreline Length |
3,830 mi /
6,164 km (including islands) |
| Water Surface Area |
23,000 square mi /
59,565 square km |
| Surface Area in
U.S. |
9,111 square mi /
23,600 square km |
|
Retention/Replacement Time |
22 years |
| Outlet |
St. Clair River to
Lake Erie |
|
Population |
1.5
million U.S. /
1.5 million Canada |
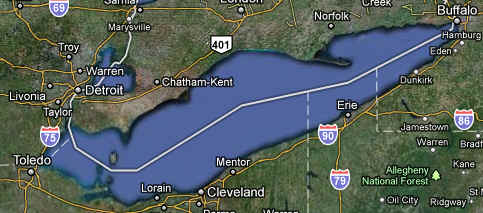
- Lake Erie is 210 feet
deep and 240 miles long. Lake Erie is the smallest of the lakes in
volume and is exposed to the greatest effects from urbanization and
agriculture. Because of the fertile soils surrounding the lake, the area
is intensively farmed. The lake receives runoff from the agricultural
area of southwestern Ontario and parts of Ohio, Indiana and Michigan.
Seventeen metropolitan areas with populations over 50,000 are located
within the Lake Erie basin. Although the area of the lake is about
26,000 km2 (10,000 square miles), the average depth is only about 19
meters (62 feet). It is the shallowest of the five lakes and therefore
warms rapidly in the spring and summer, and frequently freezes over in
winter. It also has the shortest retention time of the lakes, 2.6 years.
The western basin, comprising about one-fifth of the lake, is very
shallow with an average depth of 7.4 meters (24 feet) and a maximum
depth of 19 meters (62 feet)
Lake
Erie Basin Statistics
| Length |
241 mi
/ 388 km |
|
Breadth |
57 mi
/ 92 km |
| Depth |
62 ft / 19 m
average
210 ft / 64 m maximum
|
| Volume |
116
cubic mi /
483 cubic km |
|
Shoreline Length |
871 mi
/
1,402 km (including islands) |
| Water
Surface Area |
9,910
square mi /
25,655 square km |
|
Surface Area in U.S. |
4,977
square mi /
12,893 square km |
|
Retention/Replacement Time |
2.6
years |
| Outlet |
Niagara River and Welland Canal |
|
Population |
10.5
million U.S. /
1.9 million Canada |
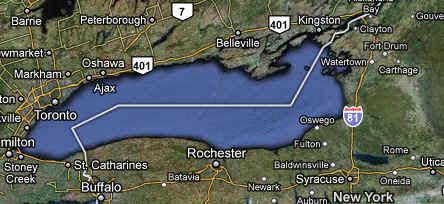
- Lake Ontario is 802 feet
deep and 193 miles long. Lake Ontario, although slightly smaller in
area, is much deeper than its upstream neighbor, Lake Erie, with an
average depth of 86 meters (283 feet) and a retention time of about 6
years. Major urban industrial centers, such as Hamilton and Toronto, are
located on its shore. The U.S. shore is less urbanized and is not
intensively farmed, except for a narrow band along the lake
Lake
Ontario Basin Statistics
| Length |
193 mi
/ 311 km |
|
Breadth |
53 mi
/ 85 km |
| Depth |
283 ft / 86 m
average
802 ft / 244 m maximum
|
| Volume |
393
cubic mi / 1,639 cubic km |
|
Shoreline Length |
712 mi
/
1,146 km (including islands) |
| Water
Surface Area |
7,340
square mi /
19,009 square km |
|
Surface Area in U.S. |
3,560
square mi /
8,960 square km |
|
Retention/Replacement Time |
6
years |
| Outlet |
St. Lawrence
River to the Atlantic Ocean
Levels regulated
by international agreements
|
|
Population |
2.8
million U.S./2.8 million Canada |
EPA Great Lakes website
Credit: EPA,NASA
|












